Historical earnings, on the other hand, are set in stone but may not fairly represent a company’s legitimate growth potential. Regardless of its historical EPS, investors are willing to pay more for a stock if it is expected to grow or outperform its peers. In a bull market, it is normal for the stocks with the highest P/E ratios in a stock index to outperform the average of the other stocks in the index. In this example, that could increase the EPS because the 100 closed stores were perhaps operating at a loss. By evaluating EPS from continuing operations, an analyst is better able to compare prior performance to current performance.
) Retained Earnings Per Share
The most crucial aspect of earnings per share comprehension is knowing how to do the calculation. In this chapter, we will look at how to calculate a company’s various earnings per share. The carrying value earnings per share, also known as book value earnings per share, reveals the company’s worth or equity in each share. Though, there are specific steps the shareholder 9 best accounting software for ecommerce companies best ecommerce software must take before converting this type of preferred share to a common one. Oftentimes, those who hold a preferred cumulative share are given some form of compensation for the unreasonable delay in receiving their dividends. Because of their right to vote for corporate policies and elect board members, common shares are also known as ordinary shares or voting shares.
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
As demonstrated in the example, if a company’s earnings per share are 200USD, then investors will be more likely to invest in that company. The similarity between a common share and a convertible preferred share that may be converted must first be stated plainly. This implies that preferred shareholders do not have the ability to vote for the board of directors or a corporate policy.
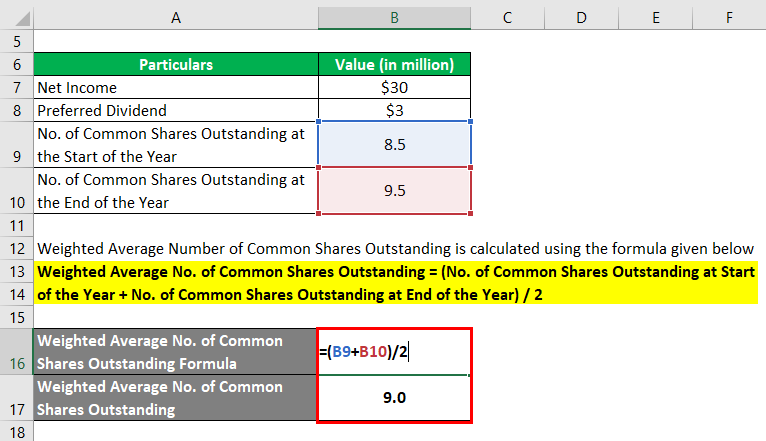
Calculating the Weighted Average Shares Outstanding
The earnings per share metric, often abbreviated as “EPS”, determines how much of a company’s accounting profit is attributable to each common share outstanding. EPS, or earnings per share, is a financial figure studied by investors, traders, and analysts. It is used to draw conclusions about a company’s earnings stability over time, its financial strength, and its potential performance. Basic EPS includes all of the company’s outstanding shares, while diluted EPS includes shares, stock options, warrants, and restricted stock units.
Calculating Earnings Per Share
The numerator of the equation is also more relevant if it is adjusted for continuing operations. If the two EPS measures are increasingly different, it may show that there is a high potential for current common shareholders to be diluted in the future. For companies with complex capital structures, it is more convenient to analyze both EPS types, basic and diluted.
Basic EPS vs. Diluted EPS: What is the Difference?

Basic Earnings per Share or Basic EPS is a profitability metric that shows how much of a firm’s net income was allotted to each share of common stock. For companies whose stocks are publicly traded, the Basic EPS is used to analyze the company’s ability to generate profits for its shareholders. When calculating the quarterly EPS for a company, using the weighted average shares outstanding for the time period may give you a better picture than the shares outstanding on the last day of the quarter. Although many investors don’t pay much attention to the EPS, a higher earnings per share ratio often makes the stock price of a company rise.
- The diluted share count differs from the basic share count in that it adds shares that aren’t yet issued — but could be.
- Since we now have the beginning and ending number of common shares outstanding, the next step is to calculate the weighted average shares outstanding.
- Again, they are anti-dilutive; if they were added to the diluted share count, loss per share would improve slightly, to $0.95.
- On the other hand, diluted earnings per share represent the profit that would be earned by each share of common stock if all dilutive securities were converted into common stock.
- Of the $250 million in net earnings, $25 million was issued to preferred shareholders in the form of a dividend.
Earnings per share (EPS), a company’s profit divided by the amount of common stock it has in circulation, is one of the most closely observed metrics in investing. Other than serving as an indicator of how much money pulled in after accounting for all expenses was allotted to each share of common stock, it’s also frequently used to determine if a company is reasonably valued. Earnings per share value is calculated as net income (also known as profits or earnings) divided by available shares. A more refined calculation adjusts the numerator and denominator for shares that could be created through options, convertible debt, or warrants.
Basic EPS is calculated by dividing a company’s net income, minus any preferred dividends, by the total number of outstanding common shares. It represents the amount of profit attributed to each share of common stock, indicating the company’s profitability on a per-share basis. Basic EPS and diluted EPS are used to measure the profitability of a company.
Divide the share price by EPS and you get a multiple denoting how much we pay for $1 of a company’s profit. In other words, if a company is currently trading at a P/E of 20x that would mean an investor is willing to pay $20 for $1 of current earnings. Notice that the preferred dividend of $50,000 has been subtracted from the income from continuing operations without impacting the gain on discontinued operations. Yes, Basic EPS can fluctuate if the number of outstanding shares changes, due to actions like stock splits or buybacks, even if the company’s net income remains constant. In the example described above, the common stockholders obtained a higher profit for each share they held in 2016 when compared to the 2015 period. This is because, like debt, they are an obligation required to be paid before the common stockholders receive dividends.

